A random forest is an Model Ensemble of Decision Trees. Take many decision trees decisions to get better result.
What is the Random Forest method;; an ensemble learning method based on constructing multiple decision trees during training and combining their predictions through averaging. Random Forests are flexibility, robustness, and ability to handle high-dimensional data, as well as their resistance to overfitting.
What is an issue with Random Forests;; susceptible to overfitting, especially when dealing with noisy or high-dimensional data. Proper tuning of hyperparameters like the number of trees and maximum depth is crucial to mitigate this.
Random forests combine multiple decision trees to improve accuracy and generalisation.
What is Random Forest, and how does it work?;; Random Forest is an method that can perform regression, classification, dimensionality reduction, and handle missing values. It builds multiple decision trees and combines their outputs. Each tree is grown using a subset of the data and features, and the final output is determined by aggregating the predictions of individual trees.
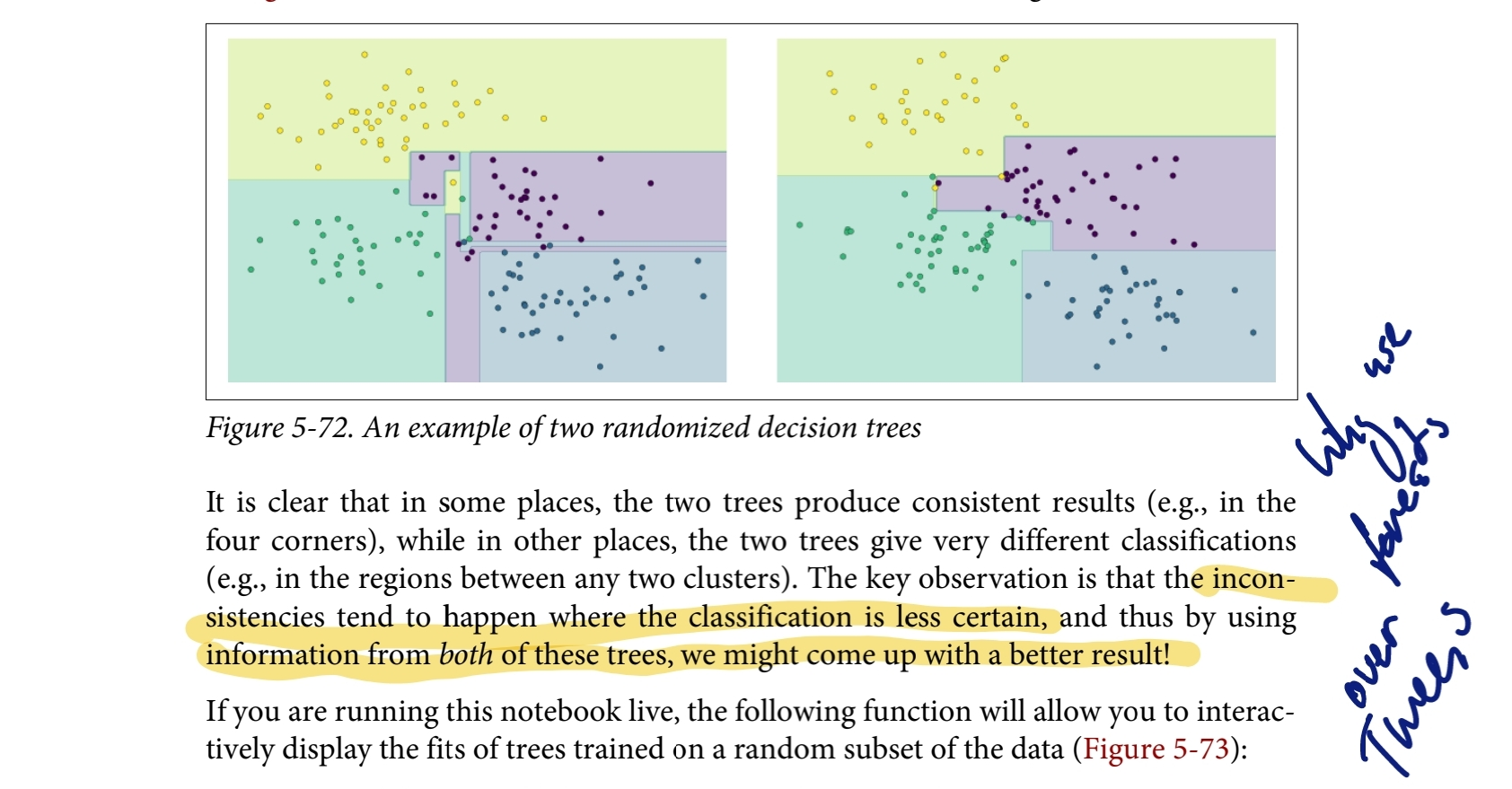
Remember that for a Random Forest, we randomly choose a subset of the features AND randomly choose a subset of the training examples to train each individual tree.
if is the number of features, we will randomly select of these features to train each individual tree.
- Note that you can modify this by setting the
max_featuresparameter.
You can also speed up your training jobs with another parameter, n_jobs.
- Since the fitting of each tree is independent of each other, it is possible fit more than one tree in parallel.
- So setting
n_jobshigher will increase how many CPU cores it will use. Note that the numbers very close to the maximum cores of your CPU may impact on the overall performance of your PC and even lead to freezes. - Changing this parameter does not impact on the final result but can reduce the training time.
What is an issue with Random Forests;; susceptible to overfitting, especially when dealing with noisy or high-dimensional data. Proper tuning of hyperparameters like the number of trees and maximum depth is crucial to mitigate this.
Decision Tree are not the best - need to make flexible for new data. THey work well with the data set they are defined on.
How to proceed with random forest: (build tree’s randomly) i.e solve the issue with decision trees. Processis called Bagging
- randomly select a dataset (bootstrap)
- randomly select two (or multiple) features for each branch and proceed like in decision tree.
variety makes trees better.
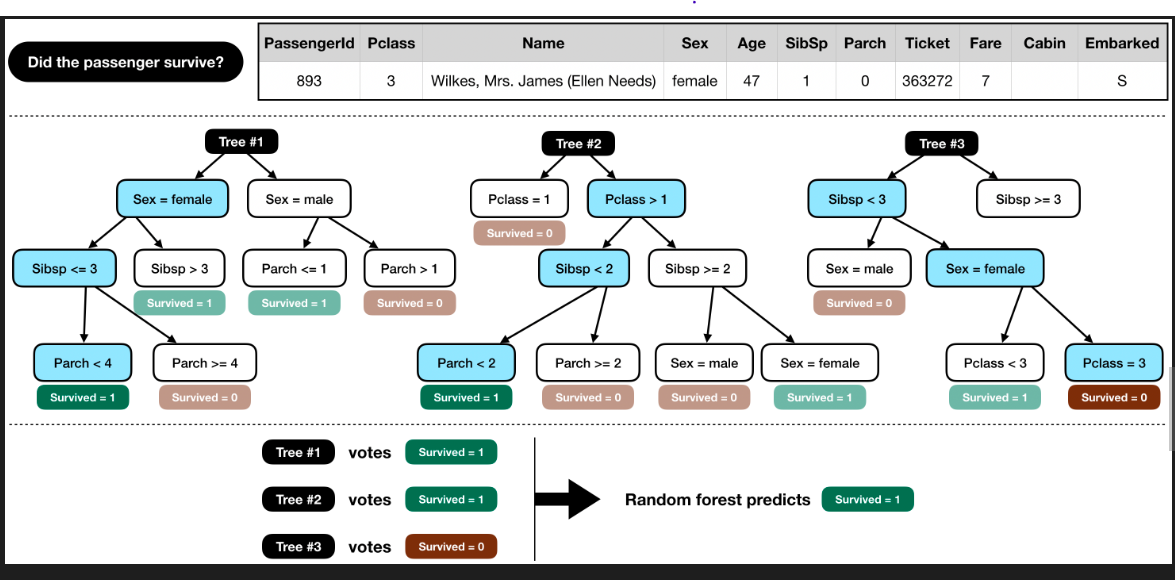
To make a prediction , run data through trees in forest, and get prediction, conclude with majority prediciton.
How to know if random forest is good ?
Use data that was not in boot strap data set - measure the accuracy based on these classiifcations.
Refine the random forest by qweaking the Hyperparameter of number of features used per step.