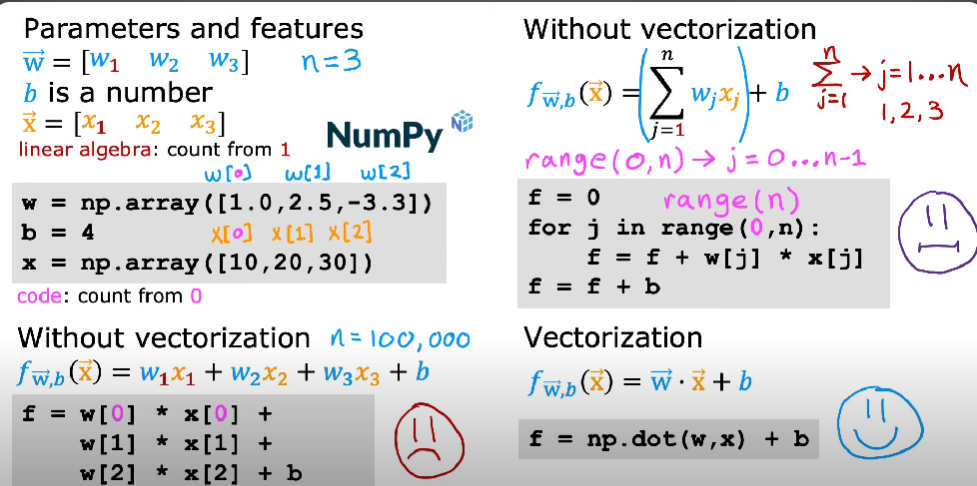
Vectorisation in Python
Vectorisation refers to the practice of replacing explicit loops with array operations, typically using libraries like NumPy. This leads to faster and more efficient code execution.
Why is NumPy vectorisation faster than a for loop?
- NumPy operations like
np.dot()are implemented in compiled C and optimised for parallel execution. - They utilise SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) and can leverage multi-threading and GPU acceleration (with appropriate backends).
- In contrast,
forloops in Python are interpreted sequentially, adding overhead and limiting performance.
Example: Dot Product
import numpy as np
a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
b = np.array([4, 5, 6])
# Vectorised
np.dot(a, b)
# Manual loop
sum([x*y for x, y in zip(a, b)])Vectorised code runs simultaneously across elements, whereas loops run sequentially.
Resources
Related: