ETL (Extract, Transform, and Load) and ELT (Extract, Load, and Transform) are two paradigms for moving data from one system to another.
ELT is most friendly for analysts
The main difference between them is that when an ETL approach is used, data is transformed before it is loaded into a destination system. On the other hand, in the case of ELT, any required transformations are done after the data has been written to the destination and are then done inside the destination — often by executing SQL commands. The difference between these approaches is easier to understand by a visual comparison of the two approaches.
The image below demonstrates the ETL approach to data integration:

While the following image demonstrates the ELT approach to data integration:
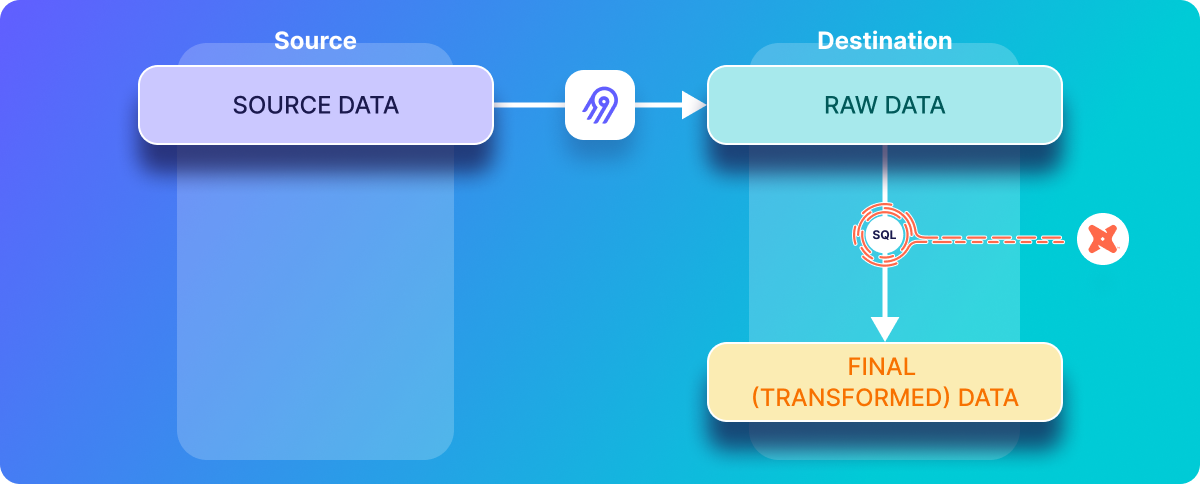
ETL was originally used for Data Warehousing and ELT for creating a Data Lake.
Disadvantages of ETL compared to ELT
ETL has several disadvantages compared to ELT, including the following:
- Generally, only transformed data is stored in the destination system, and so analysts must know beforehand every way they are going to use the data, and every report they are going to produce.
- Modifications to requirements can be costly, and often require re-ingesting data from source systems.
- Every transformation that is performed on the data may obscure some of the underlying information, and analysts only see what was kept during the transformation phase.
- Building an ETL-based data pipeline is often beyond the technical capabilities of analysts.