Vector Embedding is a technique used in machine learning and NLP to represent data in a continuous vector space. This representation captures the Semantic Relationships of data, such as words or sentences, allowing similar items to be positioned close to each other in the vector space.
Key Concepts
-
Data Compression: Embeddings compress data into a lower-dimensional space, making it easier to process and analyze. This is particularly useful for high-dimensional data like text or images.
-
Semantic Similarity: In the embedding space, similar items are positioned close to each other. This proximity reflects semantic similarity, meaning that items with similar meanings or characteristics have similar vector representations.
-
Dimensionality Reduction: Words are represented in a lower-dimensional space compared to traditional methods like one-hot encoding, resulting in more efficient computations.
-
Semantic Relationships: Words with similar meanings or contexts are located close to each other in the vector space. For example, “king” and “queen” might be closer to each other than “king” and “apple.”
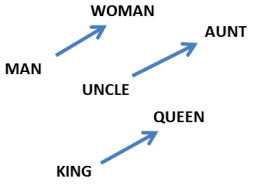
- Contextual Understanding: (Vector) Word embeddings capture the context in which words appear, allowing models to understand nuances and relationships in language.
Popular methods for generating vector (word) embeddings include:
Types of Similarity Measures
- Euclidean Distance
- Cosine Similarity
Applications
- Language Models: Vector embeddings are widely used in language models to represent words, phrases, or sentences, enabling models to understand and generate human language more effectively.
- Attention mechanism: Embeddings are often used with attention mechanisms to enhance model performance in tasks like translation, summarization, and question answering.
Example Use Cases
- Word Embeddings: Techniques like Word2Vec and GloVe create word embeddings that capture semantic relationships between words, enabling tasks like word similarity and analogy solving.
- Sentence Embeddings: Models like BERT and Sentence Transformers generate embeddings for entire sentences, facilitating tasks like sentiment analysis and semantic search.
Visualizations
- t-SNE: A technique for visualizing high-dimensional data, often used to display word embeddings in a two-dimensional space.

Implementation
How to do vector embeddings in PyTorch that show Semantic Relationships between terms.
In ML_Tools see: Vector_Embedding.py
Articles
https://blog.esciencecenter.nl/king-man-woman-king-9a7fd2935a85